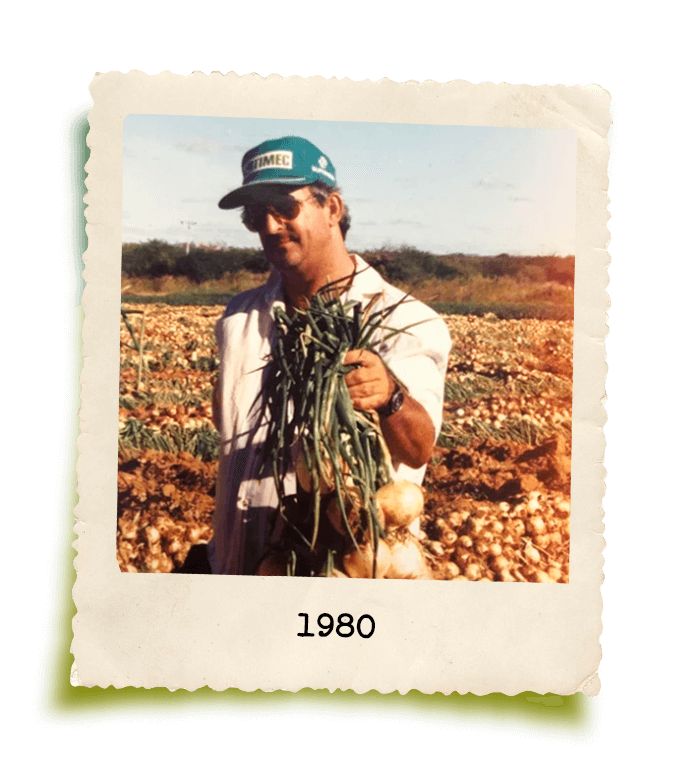
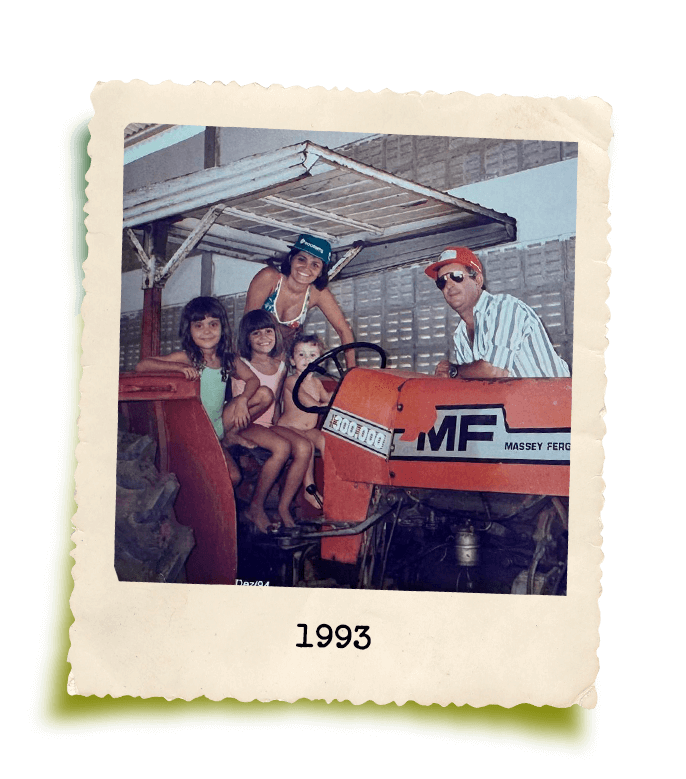
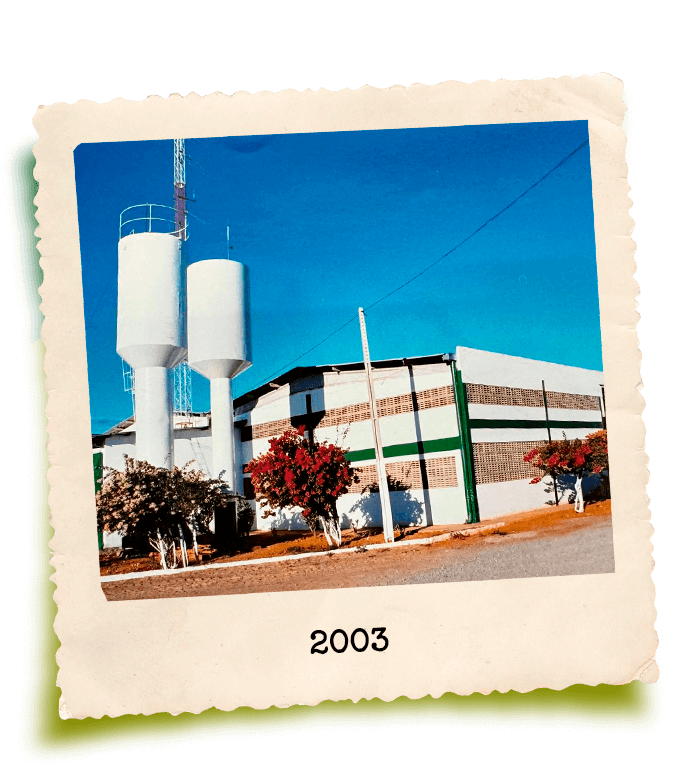
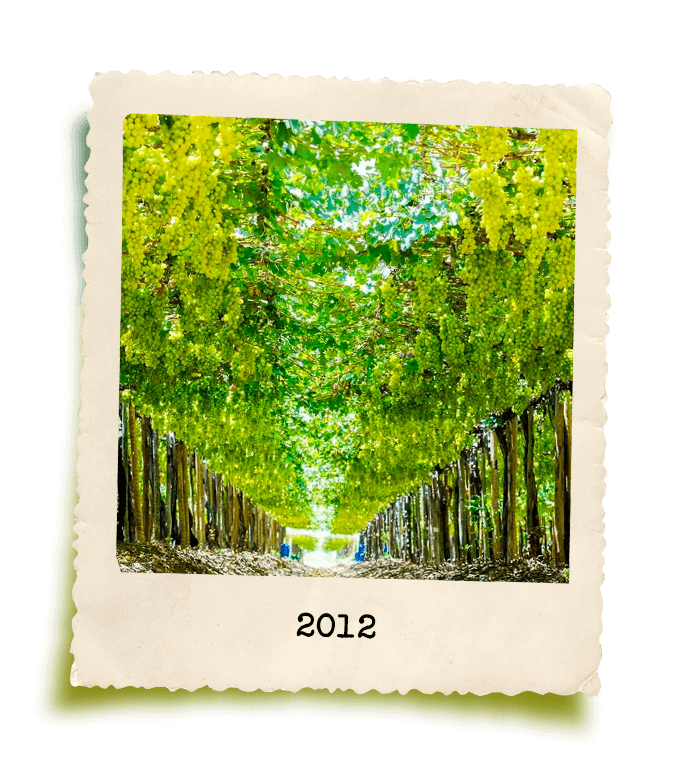
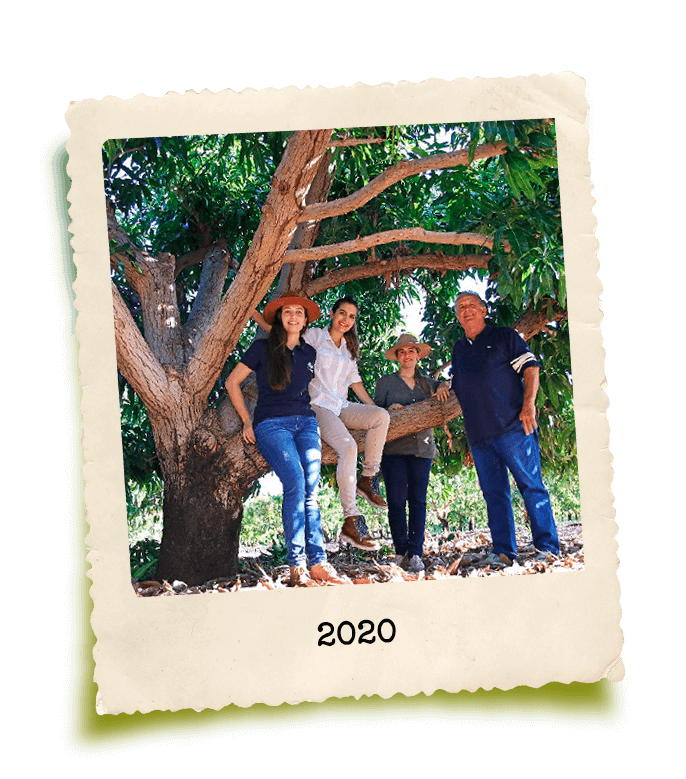
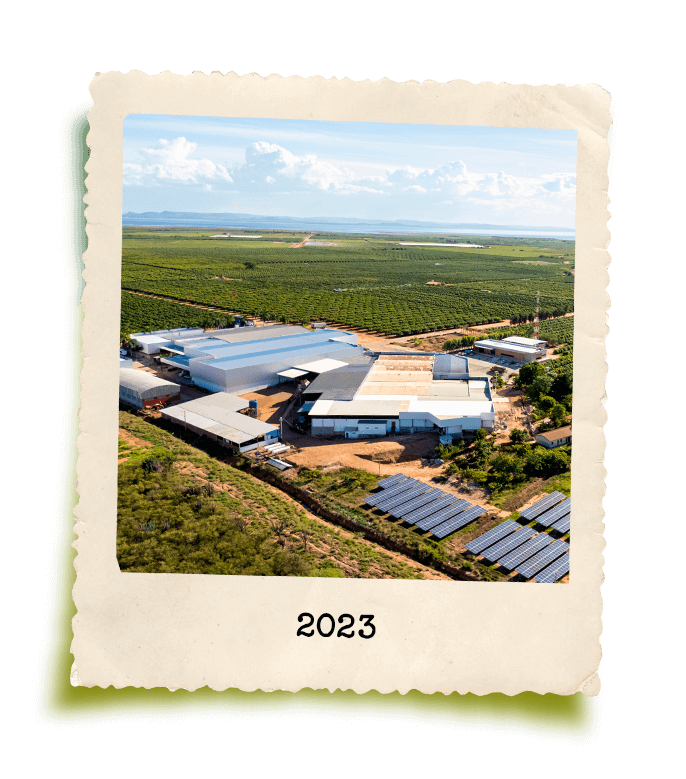








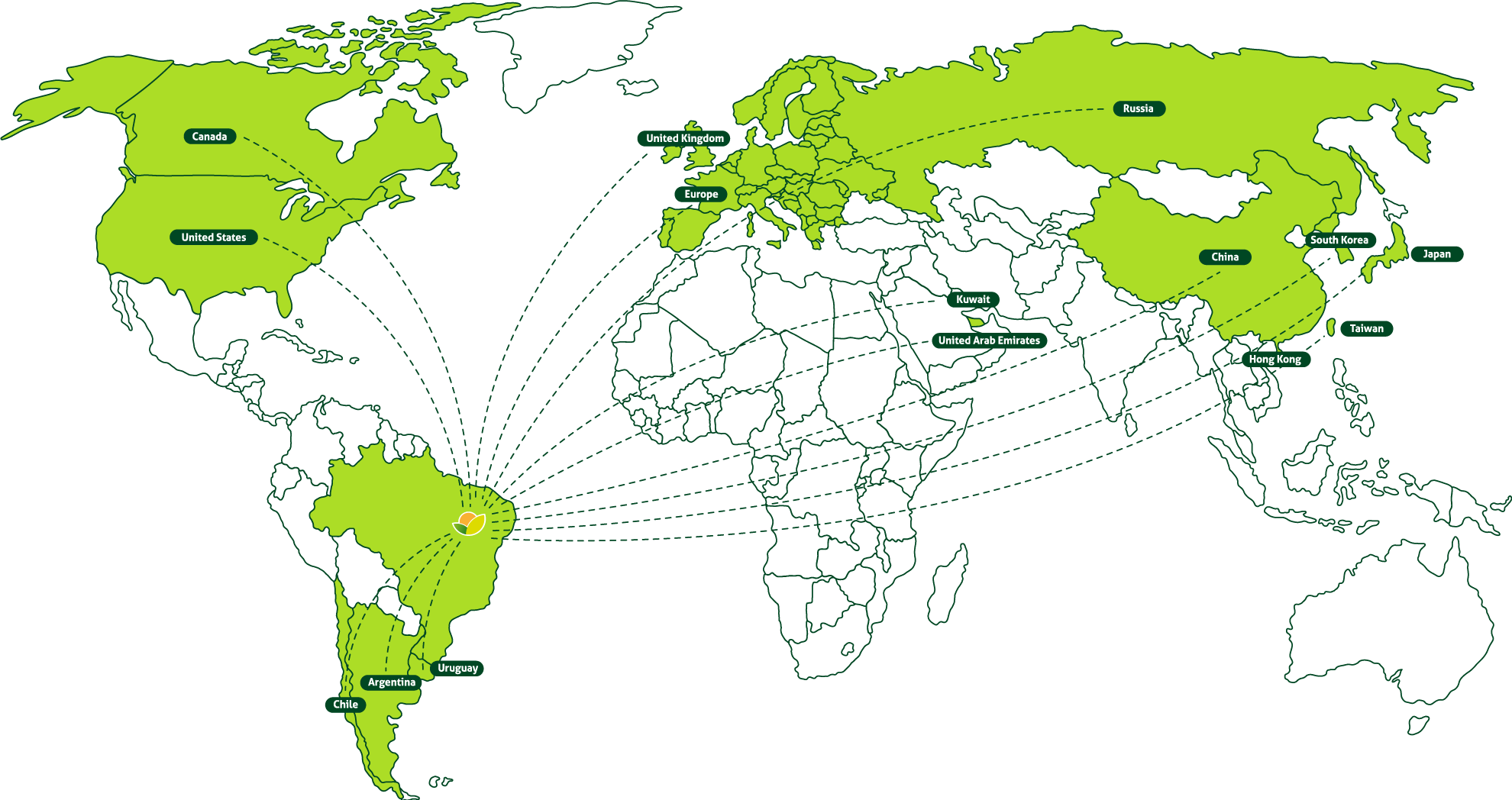
GrandValle’s story is rooted in the perseverance of its founder, Gilberto Secchi. Originally from Santa Catarina, he was one of the pioneers in fruit cultivation in the São Francisco Valley, a region in northeastern Brazil now internationally renowned for its ideal climate, soil, and water conditions for fruit production.
Despite limited resources, Gilberto Secchi formally founded GrandValle in 1988 through hard work, humility, and dedication. With over 45 years of experience in agriculture and a strong reputation in the market, GrandValle is built on a solid foundation that influences its culture and inspires everyone who is part of it. Specializing in the production of mangoes and table grapes, along with other high-quality, preservative-free products, GrandValle has grown to become one of Brazil’s leading fruit exporters.
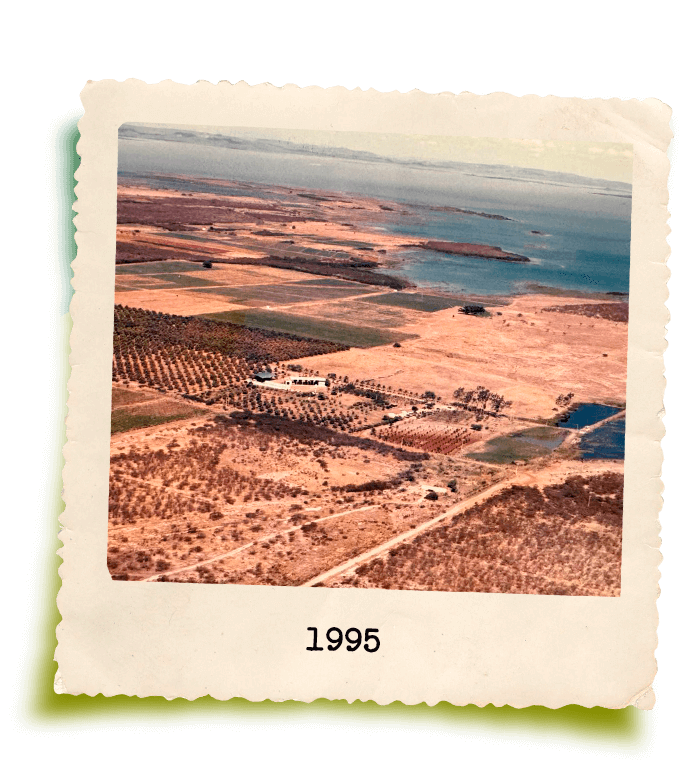
Starting with just 10 hectares of mangoes in the 1980s, the company now manages a group of farms that span over 1,000 hectares, including both productive land and environmental reserves. With a workforce of more than 1,200 employees, GrandValle recognizes its significant social role. As a result, its core values include social responsibility, environmental respect, and innovation. Every step of production, from harvesting to processing, undergoes continuous improvement and is backed by national and international certifications.




There is a reason behind the slogan “Gift of Nature”: our GrandValle TopTeam takes pride in respecting Mother Nature, which provides us with fresh fruits and many other essential resources for our health. But none of this would matter if we didn’t leave a positive legacy for the world. For this reason, strong environmental, social, and governance practices are strategic pillars of our company, which believes in sustainable agriculture—one that respects the environment, is socially fair, and fosters economic progress.
Welcome to the most exclusive brand in sustainable agriculture!
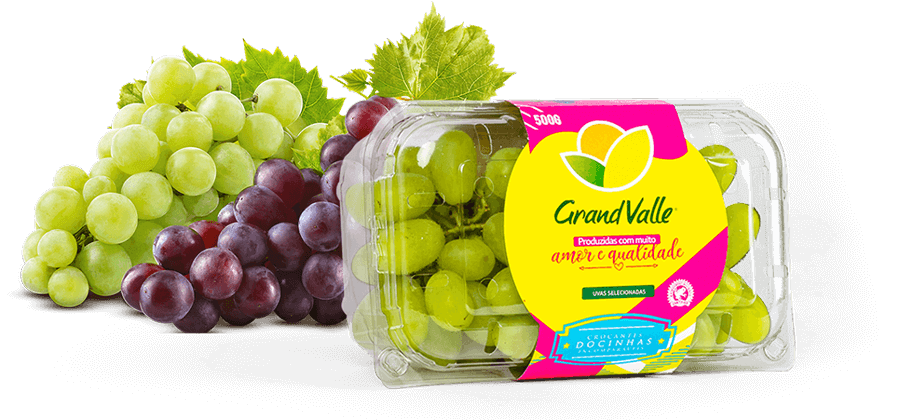




of mango production.

of table grape production.

of cold storage facilities.
of built-up area.

from the Caatinga ecosystem planted to promote local biodiversity.

A project documenting a rich photographic collection of local fauna and flora.

Greenhouse gas (GHG) emission control: the company captures more carbon than it emits.
Ongoing team training and development.
Promoting female representation in agriculture.
Utilized across our facilities.
Supporting innovation and collaboration with local educational institutions.
Promoting sports and healthy lifestyle habits.
GrandValle has set a clear agenda to strengthen the culture of environmental and social sustainability. Among the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), the company is committed to those that directly impact its operations, setting achievable targets to be implemented by 2030. This approach focuses on competitiveness, business efficiency, responsibility, and transparency.
Avoid water waste through the implementation of water reuse systems in facilities and modernization of irrigation systems. Educate staff and the local community on proper waste disposal. Reduce pollution by minimizing the use of chemicals and waste generation. Substantially increase recycling and the safe reuse of packaging materials and organic waste.
Utilize multiple energy sources, focusing primarily on renewable, efficient, and non-polluting options. Expand the use of solar energy by increasing the capacity of the current photovoltaic plant.
Promote inclusive and sustainable economic growth, ensuring freedom, equity, safety, and human dignity for all. Monitor the supply chain to prevent vulnerabilities related to human rights. Engage families and the local community in campaigns. Provide a pleasant, inclusive, and productive work environment, with investments in workplace infrastructure, training, and motivational campaigns.
Support technological development and innovation by encouraging research and partnerships with local educational institutions. Promote sustainable agriculture with a conscious use of natural resources. Encourage circular economy practices by diversifying the industry to add value to core products and commodities.
Ensure sustainable production and consumption patterns. Monitor water use and reduce inputs needed for plant management. Track performance indicators for usage and consumption, offering incentives for areas with the best results. Run awareness campaigns on responsible consumption to prevent waste and minimize environmental harm.
Protect, restore, and promote sustainable use of local ecosystems. Halt and reverse land degradation through constant soil condition monitoring. Promote the planting of native Caatinga biome species. Preserve biodiversity through pioneering research to catalog and celebrate the species of fauna and flora surrounding the company.
















ADDRESS
Fazenda Fortaleza, Rod. BR 235, KM 40
Santana do Sobrado, CEP 47300-000
Casa Nova/BA, Brazil
OPERATION
Monday – Friday | 7:00 a.m. – 4:00 p.m.
Saturday | 7:00 a.m. to 12:00p.m.
CONTACT